A Guide to Dropshipping in 2023
We tell you everything you need to know about dropshipping and how to set up a successful dropshipping business.

Dropshipping can leave you with little control over deliveries. If you’re looking to handle deliveries yourself, check out Circuit for Teams.
Dropshipping has seen a surge in popularity in recent years, resulting in a boom in dropshipping businesses — and the market is expected to keep growing.
From 2020 to 2026, the dropshipping market is anticipated to grow at a rate of almost 25 percent.
Maybe you’ve already seen people promoting their dropshipping businesses on social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok and wondered what all the fuss is about.
Dropshipping is a business model where an online retailer sells items on behalf of a supplier. When customers purchase goods online, the supplier ships the products directly to the customer.
If you have an eCommerce business, you already know how expensive it can be to produce and store inventory. Warehousing costs like rent and utilities can add up quickly.
But if you use dropshipping to fulfill orders, you can be an entrepreneur and sell online without actually holding products or shipping them to customers yourself.
With this model, you don’t purchase products until a customer order comes in — in other words, you don’t have to pay the supplier until you make a sale.
Plus, since the supplier handles the fulfillment process and sends the order directly to the customer, you don’t have to deal with pesky shipping logistics.
But how do you find a supplier to make your eCommerce business a success?
Below, I’ll explain how dropshipping works and give you the inside scoop on the pros and cons.
I’ll also answer some key questions about dropshipping that can help you set up your dropshipping business.
What is dropshipping?
Dropshipping is an order fulfillment method involving three main parties: the seller, the supplier, and the customer.
The seller is the one selling goods to customers online.
The customer is the one buying the goods.
However, the seller isn’t the one creating or selling the goods the customers purchase.
Instead, a supplier (usually a manufacturer or wholesaler) is responsible for stocking goods, fulfilling orders, and shipping products to customers.
Basically, the seller acts as a middleman between the supplier and the customer.
Sellers benefit from this business model because they don’t have to produce inventory or store it themselves.
Who’s involved in dropshipping?
To recap, there are three key players in the dropshipping business model:
- Customer: The customer is the person buying the products.
- Seller: The seller is the individual selling goods online — the dropshipper. They may have their own eCommerce website or set up a retail business on a larger seller platform like eBay, Shopify, or Amazon.
- Supplier: The supplier might be a manufacturer or wholesaler, for example. They’re the business that produces or gets goods, stocks them, and ships them to customers.
How does dropshipping work?
Dropshipping is a pretty straightforward process. Here’s what it usually looks like:
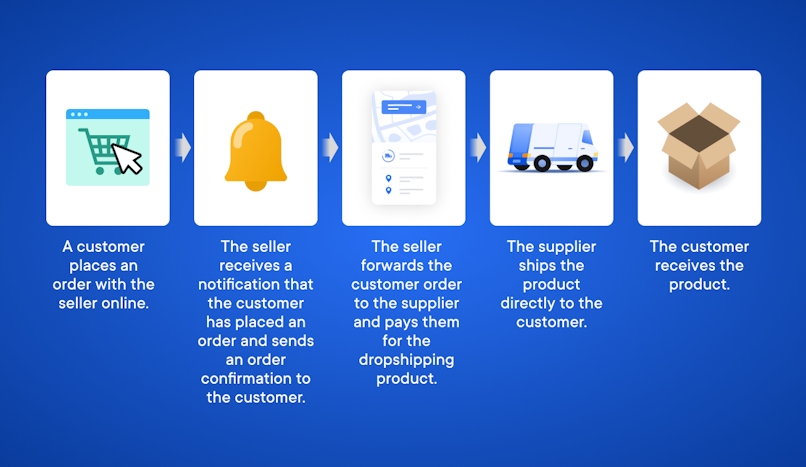
- A customer places an order with the seller online. The customer pays a set retail price, say $200.
- The seller receives a notification that the customer has placed an order and sends an order confirmation to the customer. This can include details like an order number, product description, and a link for the customer to give feedback.
- The seller forwards the customer order to the supplier and pays them for the dropshipping product. So, if the customer paid $200 for the item, the seller might pay a wholesale price of $150. You can take care of this step manually or, for less hassle, use dropshipping software that automatically notifies the supplier. Examples include DSers AliExpress Dropshipping, Spocket, SaleHoo, and Modalyst. (I’ll talk more about how to pick from these suppliers below.)
- The supplier ships the product directly to the customer.
- The customer receives the product.
What to consider before starting a dropshipping business
If you’re considering starting a dropshipping business, it’s important to consider a few things first.
Products that are in demand
You can increase your odds of dropshipping success by picking an in-demand niche that attracts a lot of potential consumer interest.
According to Shopify’s research, the best dropshipping products for 2022 are:
- Health and personal care
- Wardrobe and accessories
- Kitchen and grocery
- Home and bedroom
- Office products
- Tools and home improvement
- Camera and cellphone accessories
- Gaming
- Car accessories
That said, these trends can change. How can you identify trendy products right now? Google Trends can help.
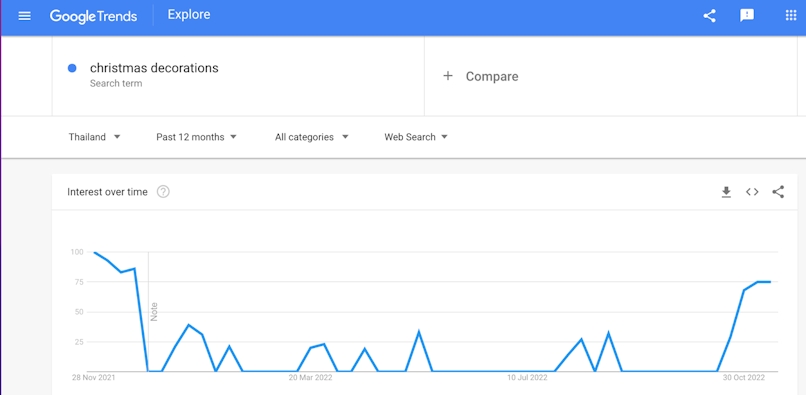
Just enter the name of the product you want to sell, set the time period, and Google Trends will show you how many people are searching for that product.
Here’s an example: You can see that searches for Christmas decorations go up significantly after Halloween.
Shipping complexities of products
Not all products are suited for dropshipping.
You don’t want to build a business around copyrighted goods, for example. This could include replicas of designer brands or items depicting copyrighted figures from movies or TV.
Hawking knock-offs can mean serious legal trouble.
Case in point: This Oklahoma man learned the hard way when he was arrested for selling fake Pokémon cards.
Aside from copyrighted products, you’ll need to make sure your supplier has the right packaging for fragile or heavy goods, which can break during shipping.
You may also want to steer clear of technically complicated items like phones or computers.
Why? Since you can’t quality control these kinds of complex tech goods, there’s no way to verify they work properly.
And if customers receive technology that doesn’t work, your business will be on the line — not your supplier.
Finding a reliable supplier
The supplier plays a pivotal role in the dropshipping process. Without them, you won’t be able to get goods to customers.
You also want a supplier to offer high-quality products and ship them securely so they don’t show up damaged at the customer’s home.
Customers won’t be too happy if they get broken products — and you’re the one they’ll complain to if they do.
They may also leave bad reviews, steering new or returning customers away from your business.
Reviews matter: Most customers read online reviews before they buy something.
To avoid these problems, research suppliers to make sure they’re trustworthy and reliable before picking one.
Some dropshipping platforms have data about individual vendors that let you see details like:
- If the vendor is verified, which lets you make sure they’re not a scam that will just take your money
- How much turnover the vendor does, which can indicate their ability to meet high demand
- Where the vendor is located and what their response time to questions is, which is good to know if you have to reach out to them with concerns
- The vendor’s success rate of shipments, so you can determine how likely it is the products they send will reach customers
- Reviews from real-world customers
Popular platforms with a lot of vendors to choose from include:
Here’s a list with reviews of these platforms and others.
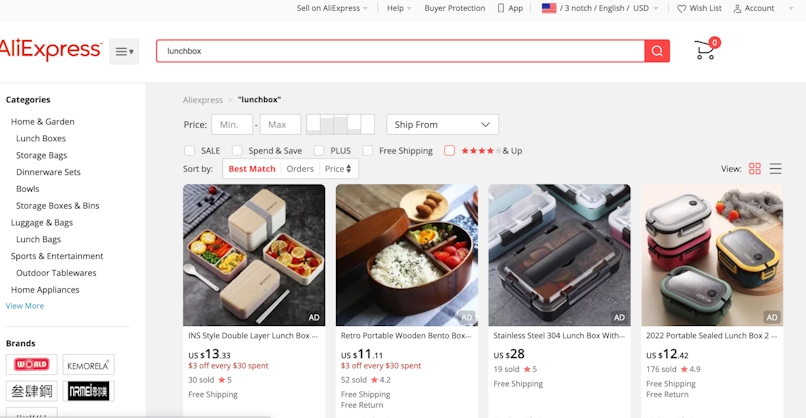
One way to research suppliers is directly through a platform like AliExpress — one of the world’s largest dropshipping platforms, with more than 100 million products ready to sell.
Type the name of the product you want to sell and tick the “4 stars and up” box, as shown below.
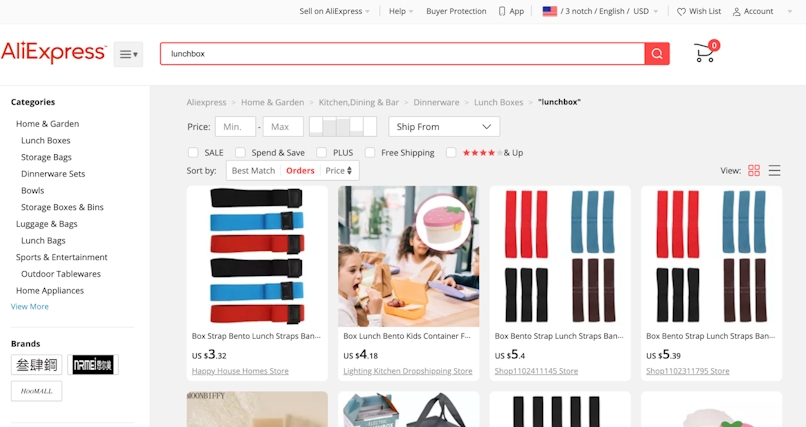
Then, sort the results by the number of orders.
Prioritize suppliers who consistently deliver plenty of orders — a testament to their experience and proficiency.
Then, click on specific suppliers to check their feedback scores, customer reviews, and shipping details.
Of course, AliExpress is only one dropshipping platform of many.
The process for verifying individual suppliers on other platforms is similar to what I’ve described for AliExpress above.
With Alibaba, you can click on the product you want to sell and get a list of suppliers. Here's an example for socks:
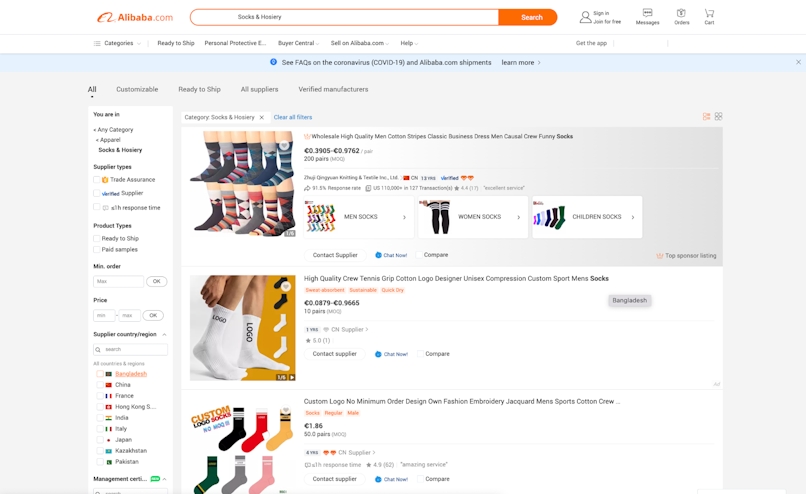
You can click on individual suppliers and see things like:
- Location
- Store rating
- Response time
- On-time delivery rate
- Total transaction revenue
Choosing a good eCommerce platform
It’s also important to choose the right eCommerce platform to sell your goods.
You can create your own retail website using a tool like Wix, Squarespace, or WordPress. These website builders come with free templates, sparing you the headache of web coding.
Register your account and pick the right template, then fill in the details (for example, product descriptions and pictures).
Here’s an example of a Wix template for a T-shirt store:
Check out these helpful resources for more information:
Making a website with a template tool is only one option. You’ll probably get more eyes on your products by listing them on platforms like Shopify, Amazon, and BigCommerce.
Consumers are already browsing these eCommerce platforms to look for products, making it more likely they’ll find you.
You can set up your own digital storefront on each of these platforms — I’ll explain how below.
Which one is right for you? Consider details like:
The type of products they offer
If a platform focuses on home goods and you sell electronics, it’s not a great match.
Consumers will associate the platform with home goods and won’t go there looking for the goods you are selling, meaning less demand.
Plan cost
Platforms like Amazon, Shopify, and BigCommerce charge you to sell through them. Research pricing.
Here are pricing details for:
For example, if you choose an Amazon individual account, you pay $0.99 for every sale. If you choose an Amazon professional plan, you pay $39.99 per month, no matter how much you sell.
Other fees
In addition to charging a plan cost, these platforms may charge other fees.
For example, Amazon charges a referral fee of 8 percent to 15 percent, depending on the product category.
Meanwhile, Shopify charges transaction fees of 2 percent, 1 percent, or 0.5 percent, depending on the type of plan you choose.
Read the fine print of whatever plan you choose.
You’ll need to take into account these costs and fees because they’ll impact your profits.
For example, if you source a product for $5 and sell it for $10 on Amazon, you might think that means $5 of profit. But you also have to consider the $0.99 Amazon takes for the sale (assuming you aren’t on the professional plan).
Learn more about calculating profit margins.
If possible, you might also want to get a sample from a supplier to make sure it meets your expectations in terms of quality.
This guide explains how to order product samples from platforms like AliExpress and Spocket.
Implementing SEO tactics
Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to how websites appear in Google and other search engines.
A website that’s optimized for search engines might appear on the first page of Google search results (where searchers can find it faster).
SEO matters because it makes it easier for consumers to find your online shop.
Since a lot of online stores are probably selling the same products as you, it’s good to be listed higher in the search rankings — people will find you first!
There are various ways to optimize your product pages for SEO, including:
- Adding comprehensive product descriptions
- Including keywords that people are likely to search for when looking for your products
- Incorporating clear, high-resolution product images
Google has a free beginner’s guide to SEO that can help you learn the ropes.
You can also hire SEO experts to optimize your online presence. You might want to outsource this task if you’re new to SEO and don’t have the time to figure it out.
While someone else does the SEO, you can focus on other elements of your dropshipping business, like picking a great supplier.
You can hire a dedicated SEO agency — here’s a list of agencies that focus on eCommerce SEO.
Alternatively, you can hire a freelancer (which might be cheaper) using a website like Fiverr, Freelancer, or People Per Hour.
How to start dropshipping in 7 steps
Done your due diligence and ready to start dropshipping? Follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine your dropshipping business idea
It’s helpful to pick a dropshipping business idea that’s trending or popular to make sure there’s customer demand for your products.
As mentioned, you can use Google Trends to look this up.
Another good way to stand out as a brand is to focus on high-quality, useful, and unusual products. This creates value for your dropshipping company’s brand.
For example, if you start selling general pet supplies in your store, you’ll be swallowed up by bigger stores. However, if you decide to only sell luxury products for dogs, you might have a better chance of standing out.
Here are a few tools you can use to find the right product niche for yourself:
Google Trends
Google Trends shows how many people search for a specific term on Google. On the website, designate the geographic area you’re interested in at the top right:
Then, enter the search term you’re interested in and you’ll see the search volume based on a timeline.
For example, searches for New Year’s Eve decorations go up in December:
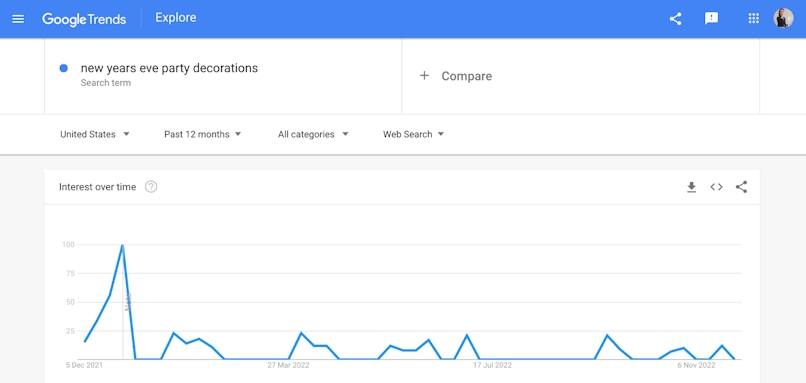
Amazon Best Sellers
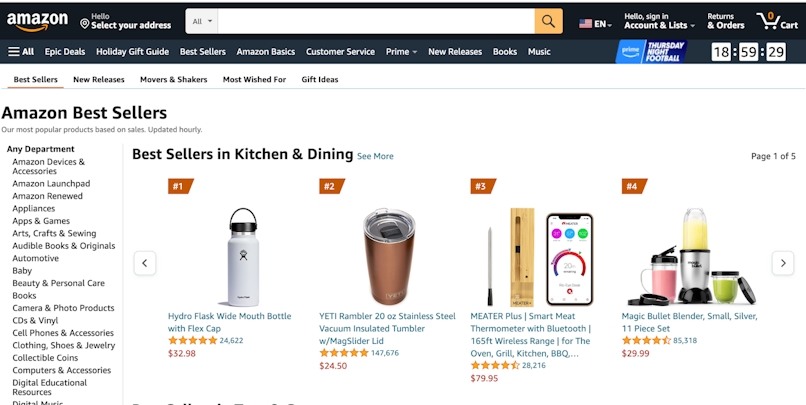
Amazon Best Sellers updates its list of top-selling products every hour. You can search various product categories to find a niche product that works for you.
Start by designating the language at the top of the page (such as American English) to narrow down your geographic target:
Then, browse bestsellers by categories like toys and games or clothes and jewelry:
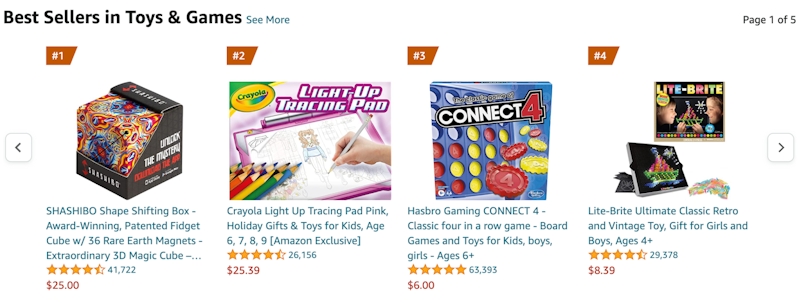
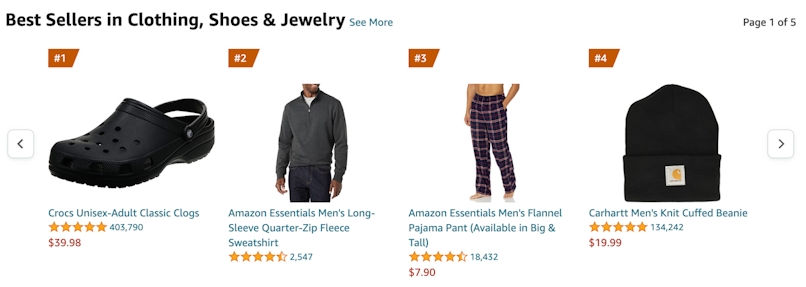
AliExpress Hot Products
Similar to Amazon, AliExpress lets you browse their fastest-selling products by categories:
Click on the category you’re interested in for details, such as fashion, electronics, or sports.
eBay WatchCount.com
WatchCount.com displays the most in-demand eBay items in real time based on users’ votes.
You can search a term and category for detailed information. For example, you might search “Christmas decorations” in “Home/Garden”:
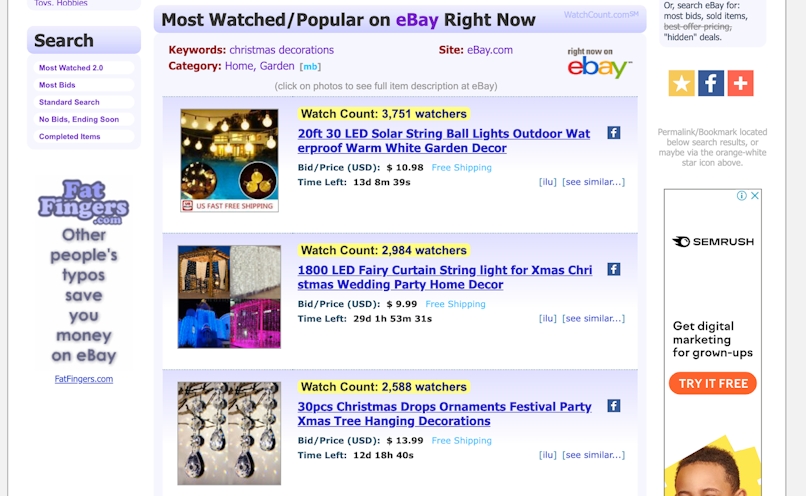
Then, you get this info:
Step 2: Legally form your business
You must set up a legal business entity before selling items online.
In addition to getting a general business license, you may also need a seller’s permit if you sell taxable goods. This depends on your state.
Registering your business isn’t just a legal must. It’s also in your interest, as it can help protect your personal liability, streamline administrative paperwork, and may offer tax advantages depending on what entity you choose.
Possible business structures include a sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), and corporation.
Note that each of these business structures has different tax implications. The US Small Business Administration (SBA) has a list of the different business structures to help you make your choice.
You’ll need an employer identification number (EIN) if you plan to hire employees for your business. This is like a Social Security number but for employers.
You can request your EIN from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It’s free — but it does take some admin work.
A lot goes into legally setting up your business (way more than we can fit into this guide!), so make sure to check out the SBA website for a more comprehensive walkthrough.
Step 3: Build your eCommerce website
Above, I talked about points to consider when picking a platform, like product offerings, base costs, and additional fees.
Once you’ve decided what eCommerce platform you want to use, you have to build your digital storefront.
Platforms like Shopify, Amazon, and BigCommerce allow you to pick your own domain name and build a website using ready-made templates.
Here are examples from these three popular platforms:
Shopify
The Shopify website builder takes you through the steps of setting up your storefront — from picking a template to choosing payment options, adding product descriptions, and uploading product images.
Just enter your email address to start. Shopify then walks you through the steps:
There’s no need to use a pricey web designer, as the Shopify store builder has ready-made themes to adjust the store’s look and feel.
Amazon
To create your own Amazon storefront, you’ll need to register for a Professional seller account and enroll in the Amazon Brand Registry as an official brand.
Then, build your online store using Amazon’s storefront builder.
This Amazon guide walks you through all the steps — including adding content (product descriptions and pictures), picking a template, and submitting your storefront for publication on Amazon.
BigCommerce
BigCommerce asks you to start building your storefront by giving basic information, like your name, email, and chosen store name (you can change it later if needed):
Then, pick a template for your store and fill in details like product descriptions and prices. The BigCommerce Page Builder editing tool lets you do this without any coding.
BigCommerce explains how it works.
Step 4: Find a dropshipping supplier
Once you’ve chosen the products you want to sell, figure out where you’ll get them.
Above, I talked about how to research dropshipping suppliers using platforms like AliExpress or Alibaba.
One consideration is user-friendliness. Many major dropshipping suppliers integrate with apps that automate elements of the dropshipping process.
For example, an app may automatically alert you when a customer order comes in and forward that customer order to the supplier.
These apps save time and minimize hassle on your part.
Note that not all apps are compatible with all platforms. This guide has a list of dropshipping apps and what platforms they can link to. For example, AliScraper works only with AliExpress.
Here are some examples of other more widely used apps:
DSers
DSers is a tool that connects to platforms like AliExpress, Shopify, and WooCommerce.
DSers links your retail platform with AliExpress to find products to sell. (Above, I described how to vet AliExpress suppliers by checking how much business they do, reading their reviews, and viewing their top-selling products).
Once you connect DSers to your Shopify account, you can use the DSers app to manage customer orders and forward them directly to the dropshipper for order fulfillment.
Dropified
Dropified is an automation app that integrates with AliExpress, eBay, Shopify, CommerceHQ, GrooveKart, BigCommerce, and WooCommerce.
It lets you fulfill orders in bulk, create unique product bundles, and even add multiple suppliers for a single product.
With this tool, you can also automate tasks from fulfillment to delivery.
Spocket
The Spocket app lets you connect directly with EU and US dropshipping suppliers so you can quickly build inventory.
It integrates with many platforms, like Wix, Shopify, BigCommerce, and WooCommerce.

With Spocket, you can automate tasks like order fulfillment. Plus, you can upgrade to a pro plan for perks like branded invoices.
Step 5: Market your dropshipping business
You’ll need to do some marketing to help drive store traffic.
Marketing helps your store stand out from the competition. Other businesses probably sell the same products — you want to give consumers a reason to choose YOU.
Here are some things to try:
Social media advertising
Social media can be a useful way of advertising your goods at no cost. It’s free to set up accounts on platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
Share information about your products, including pictures of what you sell, videos showing your goods in action, and testimonials from real-world users.
Here are some other ideas on how to use your own social media accounts to push products.
You can also use paid ads on social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram to push your products to people’s feeds. Work on creating a narrow and well-defined target audience based on age, gender, location, and interests.
You can use the Meta Ads Manager to create ads on both Instagram and Facebook.
Open the ads manager, click “Create,” pick your objective (Facebook or Instagram), and hit continue. Then, enter ad details like text and images.
Retargeting ads
Many times, customers find a product they like but don’t end up buying it. Retargeting ads allow you to re-advertise to people who already saw your ad but didn’t make a purchase.
Retargeting tools like AdRoll, ReTargeter, and Criteo can help you create inventive ads to use across several social media platforms.
For example, Adroll uses cookies (data stored in the user’s web browser) to track when they’ve visited your webpage.
With this information, AdRoll can send ads to people who have visited your page without making a purchase. Those ads might appear in the sidebars of Google search results, for example.
A company like AdRoll will integrate with your website to gather cookies and make retargeting possible.
SEO marketing
Investing in SEO marketing can help people find your store organically. SEO marketing uses keyword-heavy text content to optimize your company’s ranking on search engines.
I mentioned a few SEO techniques above, and this starter guide from Google has more details.
Influencer marketing
Getting customers to purchase from a new store can be tricky. But if you can link up with a social media influencer who can publicize your products and vouch for them, you might be able to bring some new traffic to your eCommerce store.
Research influencers who are relevant to your niche, such as pets, travel, or fashion, and reach out to them directly to see if they’re open to collaboration.
For example, you might send an influencer a direct message on Instagram to see if they want to collaborate. Some influencers also have direct email links to their agents in their bios.
You can also try platforms like Influencer Marketing Hub, Klear, or GRIN to connect. These platforms compile lists of influencers who are open to collaborations.
You can search for influencers relevant to your target audience by entering details like what you sell, demographics (age, sex, geographic location), and influencer stats (like number of followers).
Then, browse influencers and reach out to them directly on the platform to see if they want to collaborate.
Reviews
Not only are reviews a good way to receive feedback on your products and services, but they are also useful in creating social proof.
New customers are more likely to make a purchase if they can see that previous customers enjoyed their experience with your brand.
For example, you can request reviews when sending email confirmations to customers.
Step 6: Grow your dropshipping business
The great thing about eCommerce is that it’s easy to view and collect data. You can track statistics using Google Analytics.
With this tool, you can see product sales rates, average revenue per transaction, your online store’s conversion rate (that is, how many views turned into buys), and revenue and product sales trends over time.
You’ll need a Google Analytics account to set it up.
Then, go to the admin button and click on “eCommerce settings” to enable eCommerce reporting.
You’ll get a unique code to add to your eCommerce website, linking the Google account to the eCommerce site. Google Analytics can then collect and compile data.
This guide has detailed instructions with screenshots.
With information about shopper behavior, you can tailor your store’s offerings to their wants and focus on fast-moving products.
You can also see what search terms people use. This guide explains how to use your Google Analytics account for eCommerce tracking.
This can help you tweak your SEO and adapt your product offerings.
As your store grows, you also want to find ways to help it run more smoothly. Automation is one option and can cut down on time spent processing orders.
Apps can help turn manual and repetitive tasks into simple, automated tasks (like sending order confirmation emails to customers).
I talked about some of these apps above, including DSers, Dropified, and Spocket.
When picking an app, make sure it will work with the supplier of your choice. This guide has a list of apps and what platforms they link to.
Benefits of dropshipping
Dropshipping is a unique business model with some key advantages. Here are some of the highlights:
Easy to start and manage
Since you don’t have to deal with technicalities like production, warehousing, material handling, inventory management, or logistics, dropshipping has a low barrier to entry.
Translation: It doesn’t take extensive training or education to use.
For example, you don’t have to learn inventory management systems or keep track of inventory yourself.
Low cost
Starting a dropshipping business doesn’t cost much — you can sign up for an eCommerce platform plan and make your own storefront for less than $100, and there’s no need to buy inventory.
For this reason, it’s financially low risk. You don’t need to invest in a warehouse (meaning rent and utilities) since there’s no inventory to manage, which cuts overhead costs.
Lean operations
With dropshipping, you don’t have to invest time, effort, or money to manufacture, store, or organize products or maintain a warehouse.
This makes dropshipping a flexible business model.
You won’t be tied down to a single location, overseeing warehouse operations. You can manage your business from anywhere — you just need the internet.
Simple to scale
Dropshipping is also easy to scale. You can ramp up operations quickly based on customer demand.
You just have to make sure your supplier has the capacity to expand.
You can get a sense of a supplier’s capacity when researching them (see “Finding a reliable supplier” above). Metrics like turnover and warehouse square footage can tell you how big a supplier is, for example.
If you want to scale up and aren’t sure about the supplier’s capacity, reach out to them first to check. You don’t want to try to sell more than your supplier can deliver, or you’ll risk angry customers when orders aren’t fulfilled in a timely manner.
Assuming the supplier has the capacity, you don’t have to personally worry about things like increasing production capacity or finding more warehouse storage space.
Diverse product availability
Dropshipping allows you to only pay for goods once a customer places an order. This means you don’t have to invest in large amounts of inventory upfront in hopes of selling it.
Your capacity planning is a lot simpler as a result. This can make it easier to hop on trends (remember the fidget spinner?) or hawk seasonal holiday items.
Dropshipping challenges
Dropshipping has its perks, sure — but, as with any business mode, it isn’t foolproof.
Here are some of the cons of dropshipping you should be aware of before jumping in:
Lack of quality control
Since you aren’t actually handling any of the products you sell, you might have little control over the quality of the product itself.
The supplier stores, packages, and ships the products. You also typically don’t have control over how products are packaged and delivered.
Since there’s no way for you to intervene in the manufacturing or fulfillment process, dropshipping can be risky when it comes to quality control.
No control over delivery services
Similarly, since the supplier handles shipping logistics in the fulfillment process, you won’t be able to control delivery services.
If you opt to cut costs by working with overseas suppliers, supply chain hurdles can get in the way. Congestion in shipping ports can cause shipping delays, for example.
You can’t control if a customer’s order is delayed, which can create frustration for customers eager to get their goods. They may leave negative reviews, which can hurt your business’s reputation.
Remember, most customers read online reviews to inform their buying decisions.
Potential lack of customer support
The lack of quality control can also create issues with customers. Customers are still placing their orders with you, so they’ll hold you responsible for issues — not the supplier.
If someone has a bad customer experience, you’re going to hear about it. (Check out our post on dealing with difficult customers.)
Super competitive
The dropshipping space is already crowded — 27 percent of online retailers are now dropshipping. So, it can be hard to differentiate yourself from other dropshippers.
This isn’t to say you shouldn’t start your own dropshipping business. A lot just depends on how well you can research the market and find innovative and under-marketed products.
For example, the brand Notebook Therapy recognized the popularity of Asian stationery products and began selling cute, simple, and pastel-colored stationery to consumers.
The 1.6 million followers they’ve amassed on Instagram are a testament to their success.
Creating a niche for yourself will give you a better chance of succeeding in dropshipping.
Supplier challenges
Since you don’t control inventory, you’re pretty much at the mercy of the third-party supplier when it comes to determining how many orders you can take.
It’s possible that a supplier might not be able to manage particularly large orders — in which case, you’ll be stuck with backorders. Similarly, sourcing products isn’t an easy job.
Find out whether a supplier is trustworthy by placing trial orders to check product quality.
Managing different suppliers and coordinating orders between them can also become a headache. Every time a supplier delays or cancels an order, it’s you who’ll have to answer to customers.
And supply chain issues can really affect your reputation. For example, if a backup in shipping results in delayed deliveries, your customers’ orders will be delayed.
This can lead to unhappy customers and possibly negative reviews.
Another important factor to consider is that while you can increase the sale price to maximize your profits, you can’t tailor production costs.
Since you’re not involved in producing the products you’re selling, you don’t have a say in manufacturing costs.

Dropshipping FAQs
Above, I covered the basic steps it takes to start dropshipping. Still have questions?
The following frequently asked questions cover some of the most common concerns of would-be dropshippers.
Is dropshipping still lucrative in 2023?
Yes, dropshipping is profitable.
For example, business owners on Shopify have been known to earn up to $10,000 in two months through dropshipping.
And eCommerce is only going to grow bigger over time.
In 2021, retail eCommerce sales were around $5.2 trillion worldwide. This figure will likely grow by 56 percent, reaching about $8.1 trillion by 2026.
Plus, we know that 27 percent of online retailers use dropshipping.
That said, dropshipping isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme. The first few months are particularly hard since it takes time to understand whether your marketing strategy is working.
You must also understand whether your product selection appeals to your intended audience.
Only after a few months does your brand become familiar to customers and they begin buying from you.
Dropshippers with a new brand generally earn $0 to $1,000 per month.
Can you start dropshipping with no money?
Yes, it’s possible to get into dropshipping with no money. This is because you don’t have to pay for inventory (and related business costs like shipping and warehousing) upfront.
Instead, you can wait for customer orders to arrive. The customers will pay for their goods, and you can use those funds to pay for dropshipping suppliers.
That said, you’ll probably want to invest in a few basics to get your dropshipping business running.
For example, you’ll need an internet connection to run an online business, and you’ll have to set up an eCommerce website or a digital storefront on a platform like Amazon or Shopify.
You might also want to invest in marketing.
The good news: You can use low-cost or free forms of marketing, like social media (which I discussed above). Then, scale up and invest more money in marketing (like paying influencers) later.
Is dropshipping legal?
Absolutely. Dropshipping is a legitimate and legal form of order fulfillment.
Just make sure you partner with trustworthy suppliers who won’t fleece you or supply poor-quality products.
You should also be familiar with the local laws of countries and states where you plan to sell products. There might be specific restrictions on the kind of items you can sell, like counterfeit goods.
Check out information posted by the Better Business Bureau (BBB) or articles posted by local authorities.
For example, this information might be relevant if you live in Michigan.
Is Amazon good for dropshipping?
The Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program is one dropshipping option.
Amazon attracts a lot of business, with 200 million unique visitors each month. This means it can be a great way to get eyes on your business. However, it also means you’ll be facing a lot of competition.
Note that Amazon takes approximately 15 percent of your revenue, which can mean low margins. So, if your profit margins are 25 percent, you’ll end up with a margin of 10 percent.
Amazon dropshipping benefits include the fact that most of their dropshipping suppliers are already vetted, you can choose from more than 30 product categories, and you’ll have zero warehousing costs.
That said, it can be hard to establish long-term connections with customers through such a massive eCommerce platform.
Plus, there are limited opportunities for customization.
You’ll have to create your digital storefront in line with the templates and guidelines they set, which can make more complicated coding — like fun animations — a challenge.
Find success with your dropshipping business
Dropshipping has become increasingly popular, and the business model is expected to grow.
With this business model, online retailers sell items on behalf of suppliers, acting as a middleman between the supplier and the customer. The seller has the benefit of not having to deal with warehousing, shipping, or order fulfillment.
One perk of dropshipping is the low cost. For example, you don’t have to deal with transportation costs. It’s also easy to start, manage, and scale up, as you don’t have to deal with practicalities like managing drivers or optimizing delivery routes.
However, it also has drawbacks, like a lack of customer service, no control over delivery, and insufficient product quality control.
If you’re considering dropshipping, following best practices can help you succeed. For example, it’s important to research in-demand products and find reliable suppliers.
The above guide lays out some more pointers and answers some of the most common questions about dropshipping stores.
With this information, you can get your own dropshipping startup off the ground. Since the business involves little to no investment, there’s nothing to hold you back!